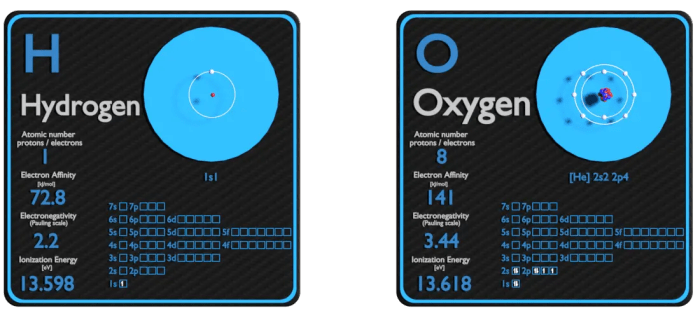
Rank the atoms below in order of increasing electronegativity. – Embark on a scientific odyssey as we delve into the fascinating realm of electronegativity, a fundamental property that governs the chemical behavior of atoms. Our quest begins with the task of ranking a diverse array of atoms in ascending order of their electronegativity, a journey that will unveil the periodic trends and factors that shape this enigmatic force.
Electronegativity, a measure of an atom’s ability to attract electrons, plays a pivotal role in determining the nature of chemical bonds, molecular structures, and chemical reactivity. Understanding the hierarchy of electronegativity is crucial for comprehending the intricate tapestry of chemical interactions that orchestrate the world around us.
Electronegativity: A Chemical Property
Electronegativity is a chemical property that describes the ability of an atom to attract electrons towards itself when it forms chemical bonds with other atoms. It is a measure of the relative strength of an atom’s pull on electrons.
Electronegativity plays a crucial role in determining the chemical properties of elements and the types of bonds they form. In general, electronegativity increases from left to right across a period (row) and decreases down a group (column) in the periodic table.
List of Atoms: Rank The Atoms Below In Order Of Increasing Electronegativity.
Here is a list of the atoms that will be ranked in order of increasing electronegativity:
- Lithium (Li)
- Sodium (Na)
- Potassium (K)
- Rubidium (Rb)
- Cesium (Cs)
- Fluorine (F)
- Chlorine (Cl)
- Bromine (Br)
- Iodine (I)
- Oxygen (O)
- Nitrogen (N)
- Carbon (C)
- Hydrogen (H)
Electronegativity Comparison
The electronegativity of an atom can be determined by its position in the periodic table. In general, the electronegativity of an atom increases from left to right across a period and decreases down a group. This is because the atomic number (number of protons) increases from left to right across a period, which increases the attraction of the nucleus for electrons.
Down a group, the atomic radius increases, which decreases the attraction of the nucleus for electrons.
Based on the periodic trend, the atoms can be ranked in order of increasing electronegativity as follows:
- Hydrogen (H)
- Carbon (C)
- Nitrogen (N)
- Oxygen (O)
- Fluorine (F)
- Chlorine (Cl)
- Bromine (Br)
- Iodine (I)
- Lithium (Li)
- Sodium (Na)
- Potassium (K)
- Rubidium (Rb)
- Cesium (Cs)
Factors Influencing Electronegativity
The electronegativity of an atom is influenced by several factors, including:
- Atomic radius:The larger the atomic radius, the lower the electronegativity. This is because the electrons are further away from the nucleus and experience less attraction.
- Nuclear charge:The greater the nuclear charge, the higher the electronegativity. This is because the nucleus has a stronger attraction for electrons.
- Shielding effects:The shielding effect is the ability of inner electrons to block the attraction of the nucleus for outer electrons. The more inner electrons an atom has, the greater the shielding effect and the lower the electronegativity.
Applications of Electronegativity, Rank the atoms below in order of increasing electronegativity.
Electronegativity is a useful concept in chemistry that can be used to:
- Predict the type of chemical bond that will form between two atoms.Atoms with large differences in electronegativity will form ionic bonds, while atoms with small differences in electronegativity will form covalent bonds.
- Explain the polarity of molecules.Polar molecules have a separation of charge, with one end of the molecule being more positive and the other end being more negative. The polarity of a molecule is determined by the electronegativity of the atoms involved.
- Understand the reactivity of molecules.Molecules with more electronegative atoms are more reactive than molecules with less electronegative atoms.
FAQ Explained
What is electronegativity?
Electronegativity is a measure of an atom’s ability to attract electrons towards itself in a chemical bond.
How does electronegativity vary across the periodic table?
Electronegativity generally increases from left to right across a period and decreases from top to bottom within a group.
What factors influence electronegativity?
Electronegativity is influenced by factors such as atomic radius, nuclear charge, and shielding effects.