The enzyme urease enhances the rate of urea hydrolysis, playing a crucial role in various biological processes. This article delves into the structure, mechanism of action, and applications of urease, providing a comprehensive overview of this fascinating enzyme.
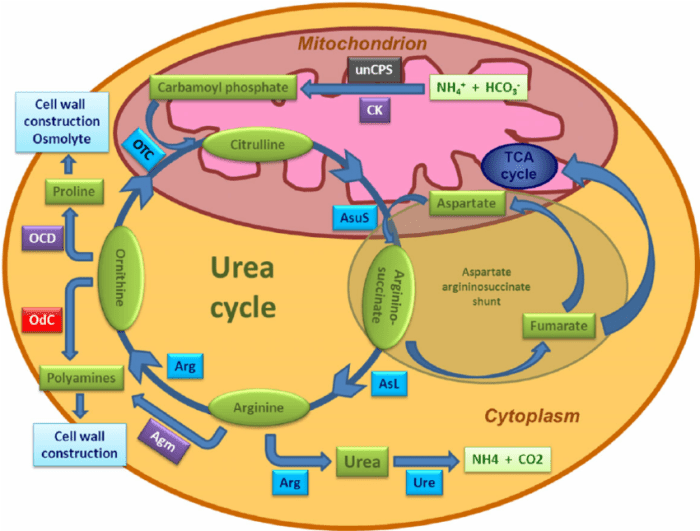
Urease is a metalloenzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of urea to produce ammonia and carbon dioxide. It is found in a wide range of organisms, including bacteria, plants, and fungi, and has significant implications in soil science, environmental monitoring, and medical diagnostics.
Urease Enzyme Introduction: The Enzyme Urease Enhances The Rate Of Urea Hydrolysis
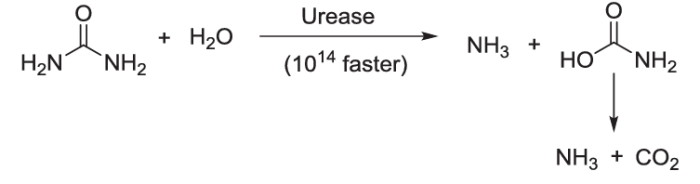
Urease is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of urea into ammonia and carbon dioxide. It is found in a wide variety of organisms, including bacteria, plants, and animals.
The structure of urease is highly conserved across different species. The enzyme is composed of three subunits, each of which contains an active site. The active site contains two nickel ions, which are essential for catalysis.
The mechanism of action of urease is well understood. The first step in the reaction is the binding of urea to the active site. The nickel ions then coordinate to the urea molecule and activate it for hydrolysis. The hydrolysis reaction proceeds through a nucleophilic attack by a water molecule on the urea molecule.
The products of the reaction are ammonia and carbon dioxide.
Factors Affecting Urease Activity
The activity of urease is affected by a number of factors, including pH, temperature, and the presence of inhibitors and activators.
The optimal pH for urease activity is around 7.5. The enzyme is less active at lower and higher pH values.
The optimal temperature for urease activity is around 37 degrees Celsius. The enzyme is less active at lower and higher temperatures.
Urease is inhibited by a number of compounds, including heavy metals, sulfhydryl reagents, and urea analogs.
Urease is activated by a number of compounds, including nickel ions and certain organic compounds.
Applications of Urease, The enzyme urease enhances the rate of urea hydrolysis
Urease has a wide variety of applications, including:
- Soil and water analysis
- Medical diagnostics
- Biotechnology
Urease is used in soil and water analysis to determine the concentration of urea in these environments.
Urease is used in medical diagnostics to detect the presence of urea in body fluids. This can be used to diagnose a variety of conditions, including kidney disease and urinary tract infections.
Urease is used in biotechnology to produce a variety of products, including ammonia, carbon dioxide, and fertilizers.
Structural and Functional Analysis of Urease
The structural and functional analysis of urease has been extensively studied. This research has led to a detailed understanding of the enzyme’s structure, function, and mechanism of action.
The structure of urease has been determined by X-ray crystallography. The enzyme is composed of three subunits, each of which contains an active site. The active site contains two nickel ions, which are essential for catalysis.
The function of urease has been studied by a variety of techniques, including enzyme kinetics, mutagenesis, and molecular modeling. These studies have shown that urease catalyzes the hydrolysis of urea into ammonia and carbon dioxide.
The mechanism of action of urease has been elucidated by a combination of experimental and theoretical studies. These studies have shown that the hydrolysis of urea proceeds through a nucleophilic attack by a water molecule on the urea molecule.
Future Directions in Urease Research
There are a number of future directions in urease research. These include:
- Engineering urease enzymes with enhanced activity
- Exploring the role of urease in nitrogen cycling and environmental sustainability
- Identifying emerging applications of urease in various fields
Engineering urease enzymes with enhanced activity is a promising area of research. This research could lead to the development of new and improved applications for urease.
Exploring the role of urease in nitrogen cycling and environmental sustainability is another important area of research. This research could lead to a better understanding of the role of urease in the environment and to the development of new strategies for managing nitrogen pollution.
Identifying emerging applications of urease in various fields is also an important area of research. This research could lead to the development of new and innovative uses for urease.
Essential FAQs
What is the active site of urease?
The active site of urease contains two nickel ions coordinated by three histidine residues and one aspartate residue.
How does urease affect soil fertility?
Urease plays a crucial role in the nitrogen cycle by converting urea in the soil into ammonia, which can be utilized by plants.
What are the potential applications of urease in medicine?
Urease has potential applications in the diagnosis and treatment of urinary tract infections and in the development of biosensors for urea detection.